William Smellie (obstetrician)
William Smellie | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 5 February 1697 Lesmahagow, Scotland |
| Died | 5 March 1763 (aged 66) Lanark, Scotland |
| Nationality | Scottish |
| Alma mater | University of Glasgow |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Obstetrics, anatomy |
William Smellie (5 February 1697 – 5 March 1763) was a Scottish obstetrician and medical instructor who practiced and taught primarily in London. One of the first prominent male midwives in Britain, he designed an improved version of the obstetrical forceps, established safer delivery practices, and through his teaching and writing helped make obstetrics more scientifically based. He is often called the "father of British midwifery".[1]
Early life and education
[edit]Smellie was born on 5 February 1697 in the town of Lesmahagow, Scotland. He was the only child of Sara Kennedy (1657–1727) and Archibald Smellie (1663/4–1735), a merchant and burgess of the town.[2][3]
Smellie practiced medicine before getting a license, opening an apothecary in 1720 in Lanark. It was not a particularly lucrative venture, as he also sold cloth as a side business to supplement his income, but he began reading medical books and teaching himself obstetrics at this time. By 1728, he was married to Eupham Borland, who was seven years his senior.[4] In 1733 he was accepted as a member of the Faculty of Physicians and Surgeons in Glasgow. In 1739, after studying midwifery in Paris for a brief period, he established a practice and a pharmacy in London.[3] In 1741 he began presenting obstetrics lectures and demonstrations to medical students and midwives. This practice proved far more successful than his first one, and Smellie made a name for himself in London.[4][3] He then enrolled at the University of Glasgow and received his MD degree in 1745.[3]
Career
[edit]
Smellie's work helped make obstetrics more scientifically based.[5] He invented a "machine" – an obstetrical manikin – for instructing his students. It essentially functioned as a model of the birthing process, and would nowadays be referred to as a "phantom". While not an original idea, the phantom was far more accurate than previous models and allowed him to visually demonstrate midwifing techniques.[4]
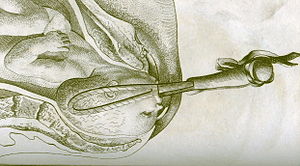
He also designed an improved version of the obstetrical forceps, which had been recently revealed after the midwifing Chamberlen family had kept it secret for generations.[4] He publicized the use of these instruments although he promoted natural birth as the best method of delivery due to its less invasive nature. In his new version of the forceps, Smellie shortened and curved the blades and included a locking mechanism.[5] In addition, he described the mechanism of labour, devised a maneuver to deliver the head of a breech, and published his teachings. He was the first person to document the natural birthing process and detailed the method by which the head of the child exited the female pelvis.[6][7]
Smellie challenged the commonly accepted concept of saving the mother over the child in times of complication. Through the introduction of forceps in the field of obstetrics, more delicate maneuvers could be performed and therefore obstetricians were able to equally weigh the life of the mother and child when complications did arise and were more often able to resolve the problem and save both. He was the first recorded figure to be able to resuscitate an infant after lung collapse and describe in detail uterine dystocia.[8]
Smellie was highly respected as a teacher as well as a midwife. Ten years after establishing his London practice, Smellie had 900 pupils and had delivered 280 lecture courses.[3] His students did not gain any certification or fulfill medical training requirements by attending his courses, but came seeking to enhance their knowledge.[4] As a teacher, Smellie tried to provide his students with live demonstrations to go along with course lectures. Consequently, he offered free midwifing services to patients if they allowed his students to observe the birthing process. This led to a more general practice of medical students attending births as a part of their medical training.[9]
One of his students, William Hunter, went on to become a well-known obstetrician and served as the physician of Queen Charlotte.[10] Unlike Hunter, Smellie was able to gain prestige and success without connections to highly reputable individuals in society. Through his humble background, Smellie was able to gain great acclaim through his interest in obstetrics and as an innovator of medical instruments and reference literature.[2]
Smellie's work was not without opposition. At the time, midwifery was a female-dominated profession. Most female midwives argued that it was inappropriate for men to assist women with childbirth, and many patients agreed. However, Smellie's work helped begin the shift of obstetrics from the work of women with some degree of experience to a medical field practiced largely by trained male physicians and surgeons.[4]
Death and legacy
[edit]Smellie taught and midwifed until 1759, in which year he retired and returned to his hometown of Lanark. He passed his practice on to Dr. John Harvie, who had married Smellie's niece. In retirement, Smellie had a residence built which he called Smellom Hall,[3] and focused on compiling and refining his findings into books, including the last volume of A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Midwifery. He died at the age of 66 on 5 March 1763, in time to finish his book but not to see it published.[4] The tomb in which Smellie (and later his wife) was buried still stands in the St Kentigern's section of the state-run Lanark graveyard.[2]
In 1828, Harvie donated a portrait of Smellie to the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh. Smellie most likely painted this portrait himself in 1719.[4]
In 1948 the Lockhart Hospital in Lanark opened a maternity department; by 1955 the entire hospital was given over to maternity services and the hospital was renamed the William Smellie Memorial Hospital. In 1992 the hospital closed and the maternity department, still called after William Smellie, was transferred to the Law Hospital in Carluke. In 2001 this unit closed and maternity services were moved to Wishaw General Hospital.[11]
Controversy
[edit]In 2010, the self-described historian[12] Don Shelton questioned the methods by which Smellie performed his research. In the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine he suggested that Smellie and his collaborator and later competitor William Hunter were responsible for multiple murders of pregnant women in order to gain access to corpses for anatomical dissection and physiological experimentation.[13] Due to the inadequate match between supply and demand of corpses, scientists had to find other means, often requiring illegal methods, to obtain access. Shelton proposed that these two physicians used what would later be named "burking", after murderer William Burke, who killed 16 people in collusion with William Hare, selling the bodies to anatomist Dr. Robert Knox.[14][7] He indicated that grave robbing was not a sufficient method by which obstetricians could access the specific type of tissue required for testing and dissection. In 1755, there was questioning of Smellie's access to corpses. Many of the accusations came from competitors, and fearing trial and even execution, Smellie stopped his work for several years in an effort to quash the suspicion that had been raised.[14][7]
Shelton's supposition was criticized by a number of medical historians who pointed out that already in 1761 Peter Camper indicated that the figures in Smellie's A Sett of Anatomical Tables "were not all from real life",[15] and very likely other methods than murder were available to obtain bodies of recently died pregnant women at that time.[16]
Helen King indicated that the response of the media and the internet to Shelton's publication "raised fresh questions about how medical history is generated, presented and evaluated in the media and, in particular, on the internet".[12]
Works
[edit]
- A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Midwifery (published in three volumes from 1752 to 1764) describes the mechanism of labour and how to handle the normal birthing process along with various complications that might arise.[5] The book was the first to set up procedures for ensuring the safe use of obstetrical forceps, as Smellie recognized that the forceps were a life-saving tool but best used sparingly.[9] By the time Smellie published the first volume, he had been practicing for over 30 years and had been involved in around 1,150 deliveries. The information presented in his book was illuminating, as few people at the time had so much experience in midwifing.[4]
- A Sett of Anatomical Tables (1754) was also an important contribution to the field of obstetrics. This was a compilation of Smellie's anatomical drawings depicting childbirth and pregnancy. Though only one hundred copies were printed, it was groundbreaking in its detail and anatomical accuracy.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Woods & Galley 2015, p. 158.
- ^ a b c Peel, John (23 September 2014). "Smellie, William (1697-1763), man-midwife". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/25752. Retrieved 30 January 2019. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ^ a b c d e f "Famous Lanarkians". Lanark Museum. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Smellie 1876, pp. 1–23.
- ^ a b c d "William Smellie". Vaulted Treasures: Historical Medical Books at the Claude Moore Health Sciences. 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- ^ Woods & Galley 2015, p. 184.
- ^ a b c "William Smellie". Encyclopedia Britannica. 7 December 2012.
- ^ Dunn, P.M. (January 1995). "Dr William Smellie (1697–1763), the master of British midwifery". Archives of Disease in Childhood: Fetal and Neonatal Edition. 72 (1): F77–8. doi:10.1136/fn.72.1.f77. PMC 2528415. PMID 7743291.
- ^ a b "Medicine in the 18th Century". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ Cassidy 2007, p. 137.
- ^ "Lanarkshire". Historic Hospitals. 26 April 2015. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- ^ a b Helen King (2011). "History without Historians? Medical History and the Internet". Social History of Medicine. 24 (2): 212. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ Don C. Shelton (1 February 2010). "The Emperor's new clothes". J R Soc Med. 103 (2): 46–50. doi:10.1258/jrsm.2009.090295. PMC 2813782. PMID 20118333.
- ^ a b Campbell, Dennis (6 February 2010). "Founders of British obstetrics 'were callous murderers'". The Guardian.
- ^ Janette C Allotey (1 May 2010). "William Smellie and William Hunter accused of murder …". J R Soc Med. 103 (5): 166–167, author reply 167. doi:10.1258/jrsm.2010.10k019. PMC 2862065. PMID 20436021.
- ^ Wendy Moore (1 May 2010). "Case not proven". J R Soc Med. 103 (5): 166–167, author reply 167. doi:10.1258/jrsm.2010.10k020. PMC 2862072. PMID 20436020.
Sources
[edit]- Cassidy, Tina (2007). Birth: The Surprising History of How We Are Born. Grove/Atlantic, Inc. ISBN 978-1555846220.
- Smellie, William (1876). Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Midwifery. Ed. with annotations, by Alfred H. McClintock. London: The New Syndenham Society. ISBN 9780882751597.
- Woods, Robert; Galley, Chris (2015). Mrs Stone & Dr Smellie: Eighteenth-Century Midwives and their Patients. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1781387528.
Further reading
[edit]- Glaister, John (1894). Dr. William Smellie and His Contemporaries: A Contribution to the History of Midwifery in the Eighteenth Century. Glasgow: James Maclehose & Sons.
- Speert, H (1958). Essays in Eponymy: Obstetric and Gynecologic Milestones. Macmillan.
External links
[edit]- William Smellie: A sett of anatomical tables, with explanations, and an abridgment, of the practice of midwifery (London, 1754)]. Selected pages scanned from the original work. Historical Anatomies on the Web. US National Library of Medicine.
